IF Statement
IF statements allow us to perform different actions based on the value of a field or other factors.
Comparison Operators:
=, >, <, >=, <=, <>
Logical Operators:
AND, OR, NOT
Logical operators allow us to join multiple comparison statements:
( {price} > 499 AND {price} <1000 ) OR {discount} = 1
Examples:
IF ( {price} <= 15, “Offer!”, “” )
IF ( {characteristics} :! “gluten”, ADD_TAG(“Non gluten”), DEL_TAG(“With gluten”) )
Conditions can also be embedded in the result of another formula, or have other formulas embedded inside them, for example:
IF ( SIMILARTEXT ( {Short text}, {Title} ) > 90, {Title}, {Short text} )
IF statement also allows for the nesting of other IF statements:
IF ( {price} > 499 AND {price} <1000 , IF ( {offer} = 1, MATH ( {price} - ( {price} / 4 ) ), {price} ), {price} )
Tip: We recommend the use of parentheses when using nesting of functions in conditionals. This way we will avoid causing syntax errors.
1. Misuse of operators without parentheses
Example:
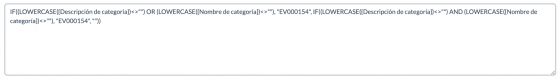
IF(LOWERCASE({complete_features_description})<>"" OR LOWERCASE({Product name})<>"", "DATO",
IF(LOWERCASE({complete_features_description})<>"" AND LOWERCASE({Product name})<>"", "DATO", ""))
As we can see in the image below, it returns the
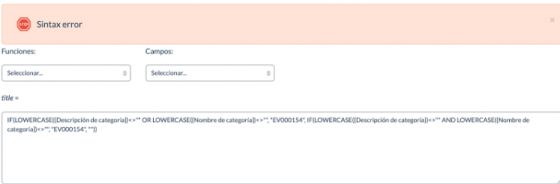
2. Proper use of parentheses
For the formula interpreter to fully recognize comparison operations, the scope of each operation must be specified in parentheses. Thus for the previous formula, we have:
IF((LOWERCASE({complete_features_description})<>"") OR (LOWERCASE({Product name})<>""), "EV000154",
IF((LOWERCASE({complete_features_description})<>"") AND (LOWERCASE({Product name})<>""), "EV000154", ""))